Electricity
Electrical charge carriers
Electrical current is electrical charge transferred in a particular time. These three properties can be calculated using the equation Q=It. Current can be a.c. or d.c.

Potential differences (voltage)
The potential difference (or voltage) of a supply is a measure of the energy given to the charge carriers in a circuit.
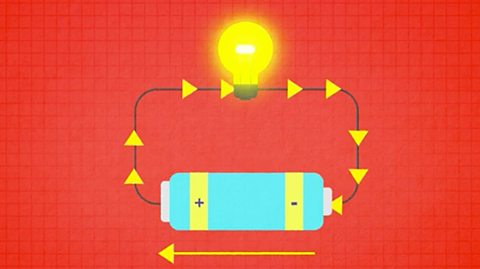
Ohm's Law
Ohm’s law relates the resistance of a component to its voltage and current. Applying circuit rules for current and voltage with Ohm’s Law allows us to formulate rules to determine total resistance.

Practical electrical and electronic circuits
Measurement and analysis of current and voltage in simple circuits allows us to formulate rules and predict unknown values.

Electrical power
Power is a measure of the rate of energy transfer and relates to the current and voltage for an electrical circuit.

Video playlist
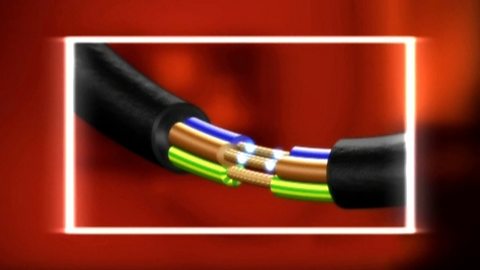
Conductors and insulators. Video
Why does a metal wire conduct electricity while the plastic sheath does not?
Links
- External linkExternal link
- External linkExternal link
- External linkExternal link
- External linkExternal link