Key points
- Stem cells are cells in animals that can continuously undergo cell division.
- embryoA bundle of several hundred cells that has developed from a fertilised ovum. are made from embryonic stem cells which can develop into any cell type.
- Adult stem cells are found only in specific areas of the body and can only develop into a limited number of cell types.
Stem cells
Video
We're all very complex organisms, made up of lots of different types of cells carrying out different jobs in our bodies; such as nerve cells, blood cells, fat cells and muscle cells.
So, where do they all come from?
Each one of us starts off as a single cell when an egg and a sperm join together. This then divides by mitosis to form two identical cells, and they just keep on dividing to form a hollow ball of 200-300 tiny cells.
Now - the clever bit.
The cells on the inside layer of this very early embryo can make all of the cell types needed in your body. They're called stem cells. The stem cells continue to divide by mitosis, and so the embryo grows. They also start to differentiate, to become specialised for different purposes.
For example, red blood cells look very different from nerve cells, but they both start out as embryonic stem cells.
Adults don't have any embryonic stem cells, but they do still have stem cells - they're essential for replacing or repairing normal cells which become damaged, or worn out. But the adult stem cells are more limited in the types of cell they can make. For example bone marrow stem cells only form different types of blood cells.
Plants have stem cells too. They're found at the meristems, the growing tips of the roots and the shoots. The big difference is that the stem cells in adult plants can still make every type of plant cell. Each one has the potential to form a whole new plant! Unsurprisingly, people want to make use of these amazing cells. Plant stem cells can be used to make clones, identical copies of the parent plant. That's massively useful for lots of things, like producing orchids and other house plants quickly and cheaply, conserving endangered species, or making clones of plants that have been genetically modified to deal with environmental stresses.
Using plant stem cells is one thing. Using human stem cells in medicine is quite another.
Scientists have found ways to grow embryonic stem cells in the lab, and are trying to use them to cure conditions such as diabetes (by replacing the insulin-producing cells in the pancreas), or enable people paralysed by spinal injuries to walk again by re-growing spinal nerves.
The clinical challenge is to encourage the embryonic stem cells to develop into the type of cells we need, without them growing into we don't want. It's ethically tricky too, because the stem cells come from human embryos.
Adult stem cells offer another possible route. Scientists have been using them for years in bone marrow transplants, and they are now investigating different types of adult stem cells, and how they might control the way they develop. After years of research scientists seem to be on the brink of success with a number of stem cell treatments which could change medicine forever.
Watch this space!
Can you answer these questions based on the video?
1. How many cells are in an early embryo?
2. What do bone marrow stem cells make?
Two to three hundred
Blood cells
Cell differentiation
Stem cells are cells that have not yet become specialised for a specific function. This process is called cell differentiation.
There are two types of stem cells in humans:
- Embryonic stem cells.
- Adult stem cells.
Embryonic stem cells
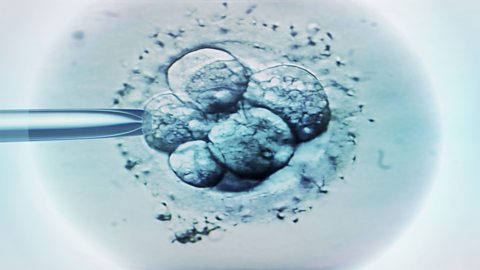
When a sperm fertilises an ovum (egg cell) a zygoteA fertilised ovum (egg cell) before it has divided into an embryo. is formed. This cell divides into two cells, then four, eight and so on. After several weeks a small bundle of cells is formed which is called an embryoA bundle of several hundred cells that has developed from a fertilised ovum.. This is made from embryonic stem cellsStem cells found in embryos that can differentiate into all cell types.. These are unusual cells because they are able to differentiate, or turn into all the different types of cell that make a human.


Did you know?
There are over two hundred different types of specialised cell that make a human.

Adult stem cells
The name adult stem cellsStem cells found in children and adults that can only differentiate into one or several cell types. is a little misleading because these are found in children as well. All stem cells that develop after the embryonic stem cells have differentiated are adult stem cells. These are different from embryonic stem cells because they are only able to differentiate into a limited number of cell types.
Adult stem cells only grow in specific parts of the body including: bone marrowThe spongy tissue found in the centre of the largest bones., breasts, intestines, fat tissue, brain, nose, hair folliclesThe tissue surrounding the root of a hair. and testes. These cells can only differentiate into the cells that grow in that region. So you could not take adult stem cells from the intestines and grow them into blood cells, for example.
Plant stem cells
Plants also have stem cells. Their stem cells are only found in specific areas called meristemsThe regions of plants at their root and shoot tips where stem cells divide. at the tips of their roots and shoots. Unlike adult stem cells, all plant stem cells can differentiate into all cell types.
Uses of stem cells
Adult stem cells in humans have been used to treat diseases like leukaemiaA cancer of the white blood cells. and other cancers of the blood and bone marrow by transplants. Theoretically the use of stem cells could treat a large range of diseases like type 1 diabetesThe pancreas produces little or no insulin so sufferers have to inject this hormone to lower their blood glucose., Parkinson's diseaseA medical condition where some brain cells die, resulting in shaking, stiffness and slowness of movement. and brain and spinal cord injuries. However this is proving difficult to do. Because adult stem cells can only differentiate into one or several cell types they are not as useful as embryonic stem cells. However the use of embryonic stem cells has clinical, and social issues associated with them.
The use of plant stem cells does not have the same issues. All plant stem cells can differentiate into all cell types.
This means a gardener can take a of a plant stem with a small number of leaves and place it into compost. Root cells will often grow from the bottom of the stem and form a new plant. This is genetically identical to the parent plant and so is a cloneOffspring genetically identical to their parent.. This process allows large numbers of copies of rare, valuable or beautiful plants to be grown quickly and easily.
Test your knowledge
Quiz
Test questions
How are embryonic and adult stem cells different?
Embryonic stem cells are only found in embryos. They can differentiate into all the cell types that make a human.
Adult stem cells are found in children and adults. They can only differentiate into a limited number of cell types.
List some of the arguments for and against the use of stem cells.
For: They can be used to treat some medical conditions in humans. These include leukaemia, type 1 diabetes and Parkinson's disease.
Against: There are clinical, ethical and social issues around the use of embryonic stem cells.
For: Stem cells in plants are used to grow copies of rare plants and beautiful flowers.
For: Large numbers of clones can be made quickly and easily.
For: There are fewer clinical, ethical and social issues surrounding the use of plant stem cells.
GCSE exam dates 2025
Find out everything you need to know about the 2025 GCSE exams including dates, timetables and changes to exams to get your revision in shape.

More on Living organisms
Find out more by working through a topic
- count9 of 15

- count10 of 15

- count11 of 15
- count12 of 15